Dedicated server rental gives full control over a remote physical machine, which suits high-traffic sites, gaming communities, streaming projects, and data-heavy apps that need stable performance and strong security. A careful choice at the rental stage keeps pages loading fast, game sessions smooth, and sensitive data guarded even as traffic climbs.
Table of Contents
Why dedicated server rental stands out
A dedicated server is a physical box in a data center reserved for a single customer, rather than shared with many other tenants. That dedicated server rental model removes noisy neighbors and gives consistent CPU, RAM, and disk resources for every request.
In real projects, dedicated server rental turns into a safety net for busy websites: traffic spikes during campaigns do not slow page loads, checkout steps stay responsive, and dashboards keep working without random timeouts. For gaming and voice servers, dedicated server rental cuts random lag from shared environments, so players stay connected and matches feel fair.
Key reasons dedicated server rental helps a demanding project:
-
Full hardware share for a single tenant, so no unknown neighbors draining CPU or disk I/O.
-
Custom security stack for firewalls, intrusion detection, WAF rules, and hardened operating system images.
-
Steady performance for high-traffic websites, streaming platforms, or database-heavy apps that need predictable response time.
-
Long-term scaling path through stronger CPUs, extra RAM, faster NVMe drives, or extra rented servers as the audience grows.
-
For a busy site or game service, dedicated server rental keeps sessions smooth while users browse, buy, and play without stutter.
A clear hardware and workload match turns dedicated server rental from a cost line into a quiet backbone that just keeps serving traffic day and night. Once tuned, dedicated server rental supports long sessions, back-office tools, and complex queries without users feeling the load.
Key hardware choices for dedicated server rental
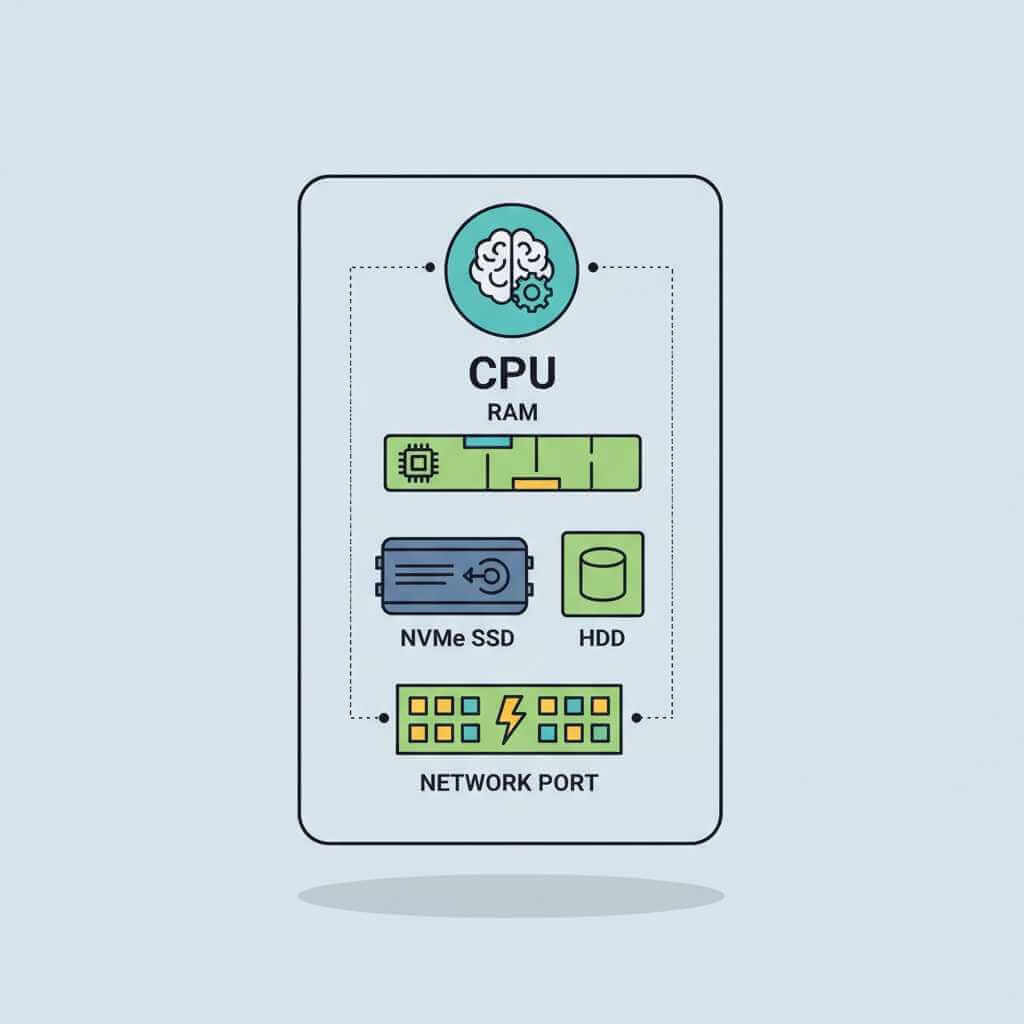
Choosing the right hardware is the core of successful dedicated server rental, because real performance comes from CPU, RAM, storage, and network shaping. A structured checklist from guides such as the Cherry Servers dedicated server guide helps match those parts to real workloads.
CPU and RAM for dedicated server rental
Processors in dedicated server rental plans usually come from Intel Xeon or AMD EPYC lines, with 8–128 cores for serious workloads. Xeon chips shine for strong single-thread speed, which helps e‑commerce frontends and APIs, while EPYC families suit massive parallel tasks and dense virtualization.
RAM in dedicated server rental should follow use case:
-
Around 16 GB for small web stacks or simple company sites.
-
Roughly 32–64 GB for e‑commerce, staging environments, or mid-size SaaS workloads.
-
64–256 GB or more for database-heavy reporting, analytics, or AI training.
ECC memory is a strong choice for production dedicated server rental, since it guards against bit-flip errors that could corrupt long-running database or cache processes.
Storage choices in dedicated server rental
Storage is where dedicated server rental upgrades feel strongest to users, because drive speed controls load time for both web pages and game worlds.
Storage comparison for dedicated server rental
| Storage type | Typical read speed | Typical use inside dedicated server rental | Cost level |
|---|---|---|---|
| HDD | Around 150–200 MB/s sequential reads. | Backup archives, logs, long term file storage; not ideal as primary disk for busy production apps. | Low |
| SATA SSD | Around 500–550 MB/s sequential reads. | General web hosting, moderate databases, VPS guests on a dedicated node. | Medium |
| NVMe SSD | Roughly 3,000–7,000 MB/s sequential reads on PCIe. | High-traffic sites, real-time analytics, game servers that stream maps and assets quickly. | Higher |
Guides from providers such as Worldstream and Melbicom stress that NVMe delivers the sharpest performance jump for dedicated server rental, especially where random I/O and many parallel queries hit the disks. For a high-traffic site or busy game world, NVMe-backed dedicated server rental turns heavy map loads, product filters, and search queries into brief waits instead of long spinners.
Network and data center location
Network ports at 1 Gbps suit many early dedicated server rental setups, but heavy streaming, VPN hubs, and CDNs push toward 10 Gbps or more. Price lists from hosts such as Database Mart show that higher bandwidth and larger traffic quotas form a big part of dedicated server rental cost, so those lines deserve close attention.
Location matters just as much:
-
A data center close to users cuts latency and keeps game pings and page loads snappy.
-
Compliance for GDPR, HIPAA, or PCI-DSS creates limits on where personal or card data may sit inside dedicated server rental setups.
-
Strong power redundancy, cooling, and physical security inside facilities featured by OVHcloud and similar providers add resilience on top of the rented hardware.
In daily work, hosting a high-traffic site on a dedicated server rental node close to its main audience keeps bounce rates low and boosts session length, simply because users see fast pages and reliable media playback.
Managed vs unmanaged dedicated server rental and OS choice
Beyond raw hardware, dedicated server rental buyers pick a management style and operating system that match skills and stack. This choice shapes who patches the box at 3 a.m., who closes new security bugs, and how hands-on daily life feels.

Managed vs unmanaged dedicated server rental
Articles from Cherry Servers, HostPapa, and Netrouting describe two clear models for dedicated server rental.
Management models in dedicated server rental
| Model | Who handles updates and security | Skills needed on your side | Typical fit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Managed dedicated server rental | Provider team handles OS patches, hardening, monitoring, and backups. | Light server knowledge; focus stays on apps and content. | Busy teams, solo founders, agencies. |
| Unmanaged dedicated server rental | Customer manages configuration, patching, and incident response; provider focuses on hardware and network. | Strong Linux/Windows admin, networking, and security knowledge. | DevOps-heavy shops, sysadmins, hosting resellers. |
For many high-traffic sites, managed dedicated server rental supplies peace of mind: the provider watches graphs, replaces failed disks, tunes basic services, and keeps backups rotating. On the other hand, experienced teams lean toward unmanaged dedicated server rental to keep root access free for custom kernels, nonstandard stacks, and hand-crafted security rules.
Real projects show a mix: a core revenue site might sit on managed dedicated server rental, while lab or staging machines stay unmanaged for freedom and cost savings. That blend gives room for experiments without risking production.
Operating system in dedicated server rental
The classic split for dedicated server rental runs between Linux distributions and Windows Server.
-
Linux choices such as Ubuntu, AlmaLinux, Debian, and Rocky Linux bring no license cost, strong performance per core, and direct fit for PHP, Python, Node.js, and container stacks.
-
Windows Server editions handle .NET, MSSQL, Active Directory, and legacy apps tightly tied to Microsoft ecosystems, at the cost of license fees and higher base resource use.
OS selection for dedicated server rental should match current apps and long-term plans, not just short-term comfort. High-traffic LAMP stacks usually feel best on Linux dedicated server rental, while fully Microsoft shops gain smoother integration from Windows-based dedicated server rental.
Security, uptime, and testing for dedicated server rental
A remote physical server draws bots and attacks from the moment it receives public DNS records, so a secure dedicated server rental layout is not optional. Providers such as Liquid Web and Worldstream outline strong defaults for firewalls, DDoS layers, and backup handling in their dedicated server rental offers.
Security for dedicated server rental
Key building blocks in a hardened dedicated server rental setup:

-
DDoS protection at network edge, using scrubbing centers and rate limits to keep floods off the server.
-
Hardware or software firewalls that filter traffic to required ports only, plus fail2ban-style agents to block abusive IPs.
-
TLS for every site or API, encryption at rest for disks storing sensitive data, and multi-factor authentication for admin panels.
-
Log collection and alerting, so attacks and resource spikes on dedicated server rental nodes reach staff before users complain.
Compliance checklists from HostPapa and DataSunrise show how dedicated server rental can meet GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS rules when logging, access controls, and encryption are set correctly. This level of setup turns dedicated server rental into a firm base for regulated projects, not just hobby sites.
Personal experience from busy online platforms shows that once those layers are in place, a dedicated server rental box rides out scanning waves and basic DDoS attempts without users noticing anything except normal load times. For gamers and shoppers, that quiet stability matters far more than any spec sheet.
Uptime, SLAs, and testing
Service Level Agreements define uptime targets, response times, and hardware replacement windows for dedicated server rental. Dataplugs and other hosts describe 99.9% uptime as a common baseline, which roughly means under an hour of unplanned downtime per month.
To keep a dedicated server rental setup honest:
-
Use third-party monitoring to ping services every minute and log real uptime, not just provider claims.
-
Run load tests such as JMeter or k6 before switching DNS, to check how the dedicated server rental node behaves under peak sessions.
-
Benchmark CPU, disks, and network on new dedicated server rental hardware, comparing results against provider marketing pages.
Over years of hosting busy sites, this style of testing before launch has stopped shaky dedicated server rental plans from going live and pushed some builds toward stronger CPUs or NVMe storage instead of cheaper disks. That up-front care saved far more than it cost in later support hours and lost sales.
Practical checklist for renting a dedicated server
Guides from TechInDeep, Liquid Web, HostPapa, Leaseweb, and others outline a repeatable flow for dedicated server rental that works for both small teams and large platforms. Adapting that flow keeps the process calm instead of chaotic.
Step-by-step dedicated server rental flow
-
Measure current usage
-
Track CPU, RAM, disk I/O, and bandwidth on your current host during both quiet hours and busy peaks.
-
Add a margin (around 25–50%) on top of that data when sketching dedicated server rental specs, so growth and traffic bursts stay covered.
-
-
Choose management level for dedicated server rental
-
Pick managed dedicated server rental if server admin time is scarce and focus stays on code, content, or community.
-
Pick unmanaged dedicated server rental if a skilled team wants full control over config and tuning, and accepts patching and incident handling.
-
-
Select hardware and OS
-
Map workloads to CPU and RAM tiers following guides from Serverion and Cherry Servers, then choose SSD or NVMe disks based on response time needs.
-
Choose Linux or Windows based on stack and licensing comfort, guided by overviews from Sectorlink, Hivelocity, and AiroServer.
-
-
Pick data center region and provider
-
Use resources such as OVHcloud’s bare-metal location guide or Truehost location notes to match dedicated server rental to your audience and compliance needs.
-
Compare pricing breakdowns from DeltaHost, ServerMania, HostPapa, WeboHosting and HostAdvice to see how CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth shape dedicated server rental bills.
-
-
Plan backup and disaster recovery for dedicated server rental
-
Follow backup practices from AccuWebHosting, Liquid Web, and Antidos: scheduled full and incremental backups, offsite storage, and recovery drills.
-
For high-traffic sites or critical game worlds, design point-in-time restore options so a bad deploy or attack does not wipe player progress or customer orders.
-
-
Migrate and test dedicated server rental before cutover
-
Use migration checklists from Cherry Servers, WIPLON, and similar sources to move files, databases, and DNS methodically.
-
Lower DNS TTL, test the new dedicated server rental copy behind hosts-file changes, then flip records and watch logs closely for at least 24–48 hours.
-
When this flow is applied, dedicated server rental turns into a steady upgrade path: shared hosting or VPS carries early growth, then dedicated server rental takes over as traffic, games, and datasets expand. For many site owners, that step is where slow page loads vanish, checkout friction drops, and users begin to trust the service to stay online.
FAQ: dedicated server rental
How does dedicated server rental work?
Dedicated server rental means you pay a monthly fee to use a full physical machine in a data center, instead of sharing resources with other customers. The provider handles hardware, power, and basic connectivity, while you focus on your sites, apps, and game servers running on that dedicated box.
How does dedicated server rental differ from VPS hosting?
VPS hosting slices one physical server into many virtual machines, so CPU and disk throughput still compete with other tenants during busy periods. Dedicated server rental gives the whole machine to you, which brings steadier performance and more control over security and software choices.
Who should consider dedicated server rental?
Dedicated server rental suits high-traffic sites, busy online stores, gaming communities, streaming projects, and data-heavy apps that outgrow shared or VPS plans. When constant slowdowns or resource limits start to hurt user experience, moving to dedicated server rental usually feels like a big relief.
Is dedicated server rental good for gaming servers and streaming?
Yes, dedicated server rental is a strong fit for multiplayer games, voice chat, and streaming setups that need low latency and predictable performance. From personal experience, hosting game worlds on dedicated server rental has kept pings low and sessions smooth even when player numbers spike hard.
How much does dedicated server rental cost each month?
Entry-level dedicated server rental often starts around the price of a mid-range VPS, then climbs as you add stronger CPUs, more RAM, NVMe storage, and bigger bandwidth packages. Research from hosting guides shows rough tiers from low three figures for simple hardware up to higher budgets for enterprise setups with 10 Gbps links and large NVMe arrays.
How do I pick the right specs for dedicated server rental?
Start by tracking current CPU, RAM, storage, and bandwidth usage, then add a safety margin so the new dedicated server rental can handle growth and peaks. From there, match your workload to CPU family, RAM size, SSD or NVMe storage, and port speed, following guidelines from trusted provider checklists.
Can I upgrade my dedicated server rental later?
Most providers allow upgrades such as extra RAM, larger or faster disks, and higher bandwidth limits on existing dedicated server rental plans. When hardware limits approach, you can also move to a stronger machine or spread load across several rented servers behind a load balancer.
How secure is dedicated server rental compared to shared hosting?
Dedicated server rental removes noisy neighbors and gives full control over firewalls, patches, and security tools, which lowers exposure to cross-account issues. Many hosts bundle DDoS filtering, backup options, and SSL support, and you can harden the system further with your own monitoring and access rules.
How long does setup and migration to dedicated server rental usually take?
Provisioning a new dedicated server rental box can take from under an hour to a day, depending on provider workflow and any custom requests. Migration of real sites or game servers tends to run over 24–48 hours counting DNS changes, testing, and a short overlap where both old and new servers stay online.
Can a beginner handle dedicated server rental, or is a sysadmin required?
Beginners can manage dedicated server rental more comfortably when they choose a managed plan, where the provider handles OS installs, updates, and security hardening. Unmanaged dedicated server rental suits those already comfortable with Linux or Windows Server, SSH, and basic networking, since daily care rests on your shoulders.
Dedicated Server Rental: Conclusion
Choosing dedicated server rental gives room for growth, steadier performance, and stronger security for any serious online project, from busy stores to packed game servers. Once the right mix of CPU, RAM, storage, and location falls into place, visitors experience quick pages, smooth matches, and stable streams instead of lag and random errors.
Dedicated server rental turns into a quiet partner for daily work: updates go through on your schedule, traffic spikes feel manageable, and sensitive data sits on hardware that you control rather than a crowded shared node. That kind of setup keeps a high-traffic site or gaming community running comfortably, so users can browse, chat, and play without worrying about slowdowns or downtime.
If the article helped clarify next steps, treat it as a checklist: review your resource usage, set a clear budget, compare a few trusted providers, and start testing a dedicated server rental plan that matches real workloads instead of guesswork. After a short trial period and some tuning, dedicated server rental can feel less like “hosting” and more like a reliable base where new features, bigger traffic waves, and fresh game seasons just fit.