The smart home revolution has moved beyond novelty into practical necessity. In 2025, the Internet of Things has evolved from isolated gadgets into an intelligent ecosystem where your smartphone, smart speakers, and connected devices work seamlessly together through artificial intelligence and edge computing. Whether you’re a tech enthusiast building your first connected home or someone curious about how AI powers these devices, understanding the technology behind modern smart home gadgets is essential for making informed purchasing decisions.
Table of Contents
The Smart Home Ecosystem: From Isolated Devices to Connected Intelligence
Just five years ago, a smart home meant having a few disconnected devices that operated independently. Today’s smart homes feature integrated systems where devices communicate continuously, learn from user behavior, and make autonomous decisions without constant human input. This transformation stems from three critical technological advances: artificial intelligence algorithms, edge computing capabilities, and improved wireless connectivity standards.
The global smart home market reflects this momentum. An estimated 30 billion IoT devices are now connected worldwide, generating unprecedented amounts of data that devices process locally rather than routing through centralized cloud servers. This shift to edge computing—processing data at or near the device rather than in distant data centers—represents one of the most significant changes in smart home technology.
Smart home devices today incorporate machine learning models directly on the hardware itself. Rather than sending raw data to cloud services for analysis, devices like modern smart thermostats perform sophisticated AI computations locally, enabling instant responsiveness and protecting user privacy by keeping sensitive information off remote servers.
AI-Powered Smart Thermostats: Learning Your Preferences
At the center of most modern smart homes sits an AI-enabled thermostat that has fundamentally changed how people manage home climate control. Unlike traditional programmable thermostats requiring manual scheduling, today’s smart thermostats function as learning devices that adapt to your lifestyle automatically.
The Google Nest Learning Thermostat (4th Generation) exemplifies this evolution, powered by Google’s Gemini AI engine. The thermostat continuously learns your preferred temperatures throughout the day and makes micro-adjustments based on detected motion, weather forecasts, and your established patterns. It recognizes when you typically arrive home and pre-cools your space minutes before you walk through the door. When the thermostat detects motion patterns suggesting you’ve left for work, it automatically shifts to energy-saving mode.
The Ecobee Premium Smart Thermostat takes the concept further by combining climate control with a built-in smart speaker featuring Alexa integration. This hybrid approach—treating the thermostat as a control hub rather than a single-function device—reflects a broader trend in smart home design where devices serve multiple purposes.
What makes these thermostats genuinely intelligent is their edge computing architecture. Rather than relying entirely on cloud connectivity for decision-making, they process temperature data, occupancy signals, and weather information locally, enabling split-second responses without network latency issues. This local processing means your thermostat continues functioning perfectly even during internet outages, a critical reliability factor for home comfort systems.
Smart Speakers and Voice Assistants: The Command Center
Smart speakers have evolved from entertainment devices into the central nervous system of connected homes. Amazon Echo, Google Nest Audio, and Apple HomePod mini serve as more than music players—they’re AI-powered hubs that control lighting, thermostats, security systems, and dozens of other connected devices through natural language voice commands.
These devices incorporate advanced on-device AI capabilities that allow them to understand complex voice commands, adapt to different user voices, and make context-aware decisions. When you tell your smart speaker to “make it cooler,” the device’s AI understands you’re addressing climate rather than temperature tone and communicates with your smart thermostat.
The Google Nest Hub Max and similar smart displays introduce computer vision capabilities, using built-in cameras with edge-based visual recognition to enable gesture control, face recognition for personalized responses, and sleep tracking without requiring cloud processing of sensitive video data. This on-device AI approach means your privacy isn’t compromised even while using advanced recognition features.

The same edge-compute shift is happening on phones too—this guide explains on-device vs cloud vs hybrid AI for smartphone chatbots and what it means for privacy and speed.
Edge Computing: The Technology Transforming IoT Responsiveness
Edge computing represents perhaps the most transformative technology underpinning modern smart home devices. Rather than sending all sensor data to cloud servers for analysis, edge computing performs calculations directly on devices or nearby local gateways. For smart home applications, this architectural shift delivers three critical advantages: reduced latency, lower bandwidth consumption, and improved reliability.
Reduced Latency means your smart devices respond instantly. When motion detects you walking into a room, an edge-computed smart lighting system triggers within milliseconds rather than waiting for cloud servers to respond. This instantaneous feedback creates the sense of genuine intelligence rather than mechanical automation.
Bandwidth Efficiency reduces the burden on your internet connection. Instead of streaming every sensor reading to cloud servers, devices filter raw data locally and transmit only actionable insights. A smart security camera might send alerts only when it detects actual intrusions rather than continuously uploading video streams. This efficiency becomes critical as homes accumulate more connected devices—over 30 billion IoT devices now exist globally, and centralizing all processing through cloud infrastructure would create severe congestion.
Resilience and Privacy emerge as edge computing removes dependencies on constant cloud connectivity. If your internet connection drops, edge-powered devices continue functioning normally—your lights still respond to motion, your thermostat still regulates temperature, and security systems remain active. Additionally, sensitive data remains on local devices rather than being transmitted to remote servers, fundamentally improving privacy compared to cloud-dependent systems.
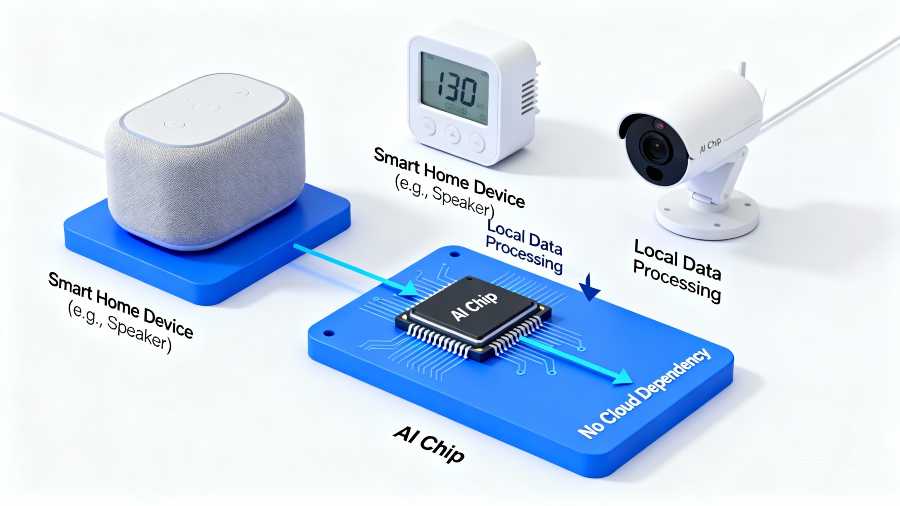
AI and Edge Computing Synergy: Smarter Decision-Making
The most powerful smart home innovations combine AI algorithms with edge computing architecture. This hybrid approach enables devices to perform sophisticated machine learning locally, adapting their behavior based on learned patterns without requiring cloud connectivity.
Behavior-based personalization represents one key application. Your smart lighting system learns that you typically increase brightness gradually each morning, so it automatically begins softly illuminating your bedroom before your alarm even sounds. Your smart blinds recognize that you prefer them closed during afternoon hours to reduce glare on your screen, so they automatically close when afternoon light reaches specific intensity levels.
Predictive maintenance uses edge AI to monitor device health continuously. Smart appliances track power consumption patterns and motor vibrations to predict failures before they occur. Your refrigerator alerts you that its compressor is beginning to wear, suggesting preventive maintenance before actual breakdown happens.
Energy optimization employs edge AI to analyze usage patterns and automatically adjust device operation for minimal energy consumption. A smart thermostat running Mitsubishi Electric‘s AI technology automatically learns the thermal characteristics of your home—how quickly it heats, where temperature variations occur, and how weather affects comfort—then adjusts HVAC operation to maintain target temperatures using minimum energy.
IoT Connectivity Standards: The Infrastructure Layer
Behind every smart device sits connectivity technology that enables communication. The industry has standardized around several IoT protocols, each with distinct advantages. Wi-Fi dominates for bandwidth-hungry devices like smart displays and cameras. Z-Wave and Zigbee offer low-power alternatives for battery-operated sensors that need years of runtime. Matter—the new universal smart home standard—promises to unify these fragmented protocols, allowing devices from different manufacturers to communicate seamlessly.
The evolution to 5G and emerging 6G standards promises ultra-low latency and higher bandwidth, enabling more sophisticated IoT deployments. Hybrid connectivity—where devices automatically switch between Wi-Fi, 5G, satellite, and other networks—represents the 2025 trend, ensuring consistent coverage regardless of location.
Smart Home Security Cameras: Privacy-Conscious AI
Modern smart security cameras incorporate edge AI that fundamentally changes how home surveillance works. Instead of recording everything and storing video in cloud servers, contemporary cameras like those from Arlo and Eufy perform visual analysis locally, detecting actual security threats and recording only relevant footage.
This edge-based approach means the camera can recognize your family members, distinguish between delivery persons and suspicious activity, and only alert you when genuine security concerns emerge. The device performs facial recognition, motion classification, and behavior analysis entirely on the local hardware using dedicated AI chips, protecting privacy while delivering sophisticated security intelligence.

Smart Home Integration: Cross-Device Coordination
The true power of modern smart homes emerges when devices coordinate their operations. Your smart lighting system communicates with motion sensors and brightness monitors to automatically adjust illumination based on occupancy and natural light levels. Your smart thermostat exchanges weather data with outdoor temperature sensors while coordinating with your smart lighting to optimize energy efficiency—adjusting blinds to reduce solar heat gain in summer or maximize it in winter.
Platforms like Google Home, Amazon Alexa, and Apple HomeKit serve as orchestration layers, enabling devices from different manufacturers to work together through unified control interfaces and automated routines. However, Apple’s AI ecosystem after the recent Apple executive shakeup, might affect these platforms as well. We will see how this turns out.
The Role of Edge AI Chips: Processing Power at the Source
Enabling sophisticated AI processing directly on consumer devices requires specialized hardware. Edge AI chips—processors specifically designed to execute machine learning models with minimal power consumption—have become standard components in modern smart devices.
These chips differ fundamentally from the powerful but power-hungry processors in smartphones and computers. Edge AI chips prioritize efficiency, performing complex computations using minimal battery power. A smart doorbell powered by edge AI can recognize faces and detect suspicious activity for weeks between battery charges, whereas cloud-dependent alternatives would exhaust batteries in days due to constant connectivity demands.
Building Your Smart Home: Practical Recommendations
For tech enthusiasts beginning their smart home journey, a strategic approach yields better results than randomly purchasing devices. Start with a smart speaker hub—either Amazon Echo, Google Nest, or Apple HomePod mini—as your command center. This single device becomes the coordinator for all future purchases.
Next, add a smart thermostat like the Nest Learning Thermostat Gen 4 or Ecobee Premium, as temperature control typically represents the largest portion of home energy consumption. The AI learning capabilities directly translate to measurable utility bill reductions—many users report 10-15% energy savings within the first month of smart thermostat installation.
Then expand strategically with smart lights from Philips Hue or LIFX (offering millions of color options and scheduling capabilities), smart plugs for converting ordinary appliances into connected devices, and smart security cameras as privacy and budget allow.
Prioritize devices supporting Matter protocol, the emerging standard that reduces vendor lock-in and ensures future compatibility as the smart home ecosystem continues evolving.

Future Trends: What’s Coming to Smart Homes
The smart home landscape continues accelerating. Federated learning—where IoT devices collaborate to improve AI models while keeping raw data private—promises more sophisticated device intelligence without centralized data collection. Decentralized mesh networks will enhance connectivity reliability by allowing devices to relay signals through each other, eliminating dead zones and expanding reliable coverage throughout large properties.
Quantum edge computing, still in infancy but approaching commercialization, promises exponential improvements in processing capability, enabling even more sophisticated local AI analysis. 5G and future 6G networks will provide ultra-low latency connectivity that enables real-time coordination between distributed smart home devices and cloud services when needed, while edge computing handles local processing.
The integration of on-device machine learning models will enable increasingly personalized behavior as devices learn individual preferences and adapt accordingly. Your entire smart home ecosystem will become progressively smarter as AI models running locally on each device improve through continuous learning.
Conclusion
The smart home technology of 2025 represents a fundamental shift from the isolated gadget approach of previous years toward integrated, AI-powered, edge-computed ecosystems where devices work together intelligently. By understanding how smart thermostats use machine learning, how edge computing enables instant responsiveness, and how AI coordination connects different manufacturers’ devices, you can make informed decisions about which technologies and devices suit your needs.
The technology underpinning modern smart homes—artificial intelligence, edge computing, IoT connectivity, and local data processing—represents the future not just of residential spaces but of computing itself. For tech enthusiasts, this moment offers exciting opportunities to experience cutting-edge technology becoming practical, affordable reality. Whether you’re optimizing home energy consumption or simply enjoying the convenience of voice-controlled everything, the intelligent connected home has arrived.